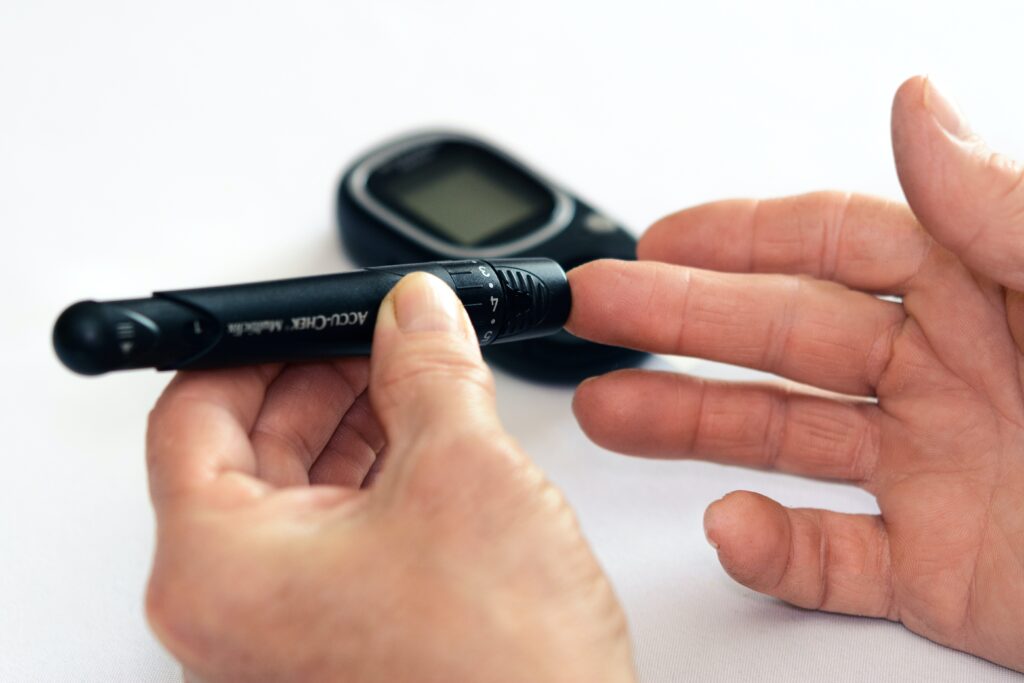
Diabetes is a chronic disease that interferes with the body’s ability to process blood sugar (glucose). Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are the two primary subtypes.
With type 1 diabetes, the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, a hormone that controls blood sugar, are attacked and destroyed by the body’s immune system. Lack of insulin is the outcome, which raises blood sugar levels.
With type 2 diabetes, the pancreas either produces insufficient insulin or the body develops a resistance to the effects of insulin. High blood sugar levels are also a result of this. [Learn How to control it?]
If left untreated, both types of diabetes can lead to major health issues such damage to the heart, kidneys, nerves, eyes, and cardiovascular system. But, with the right supervision, people with diabetes can live healthy and fulfilling lives.
Blood glucose, also referred to as blood sugar, is a form of sugar that is present in the bloodstream, and it is responsible for providing energy to the body’s cells. It is crucial to maintain healthy blood glucose levels since elevated levels can result in diabetes and other health problems. Fortunately, there are various natural methods of controlling blood glucose levels.
1. regular exercise
2. healthy diet
3. Staying well hydrated
4. stress management
5. Getting adequate sleep
6. lifestyle changes
7. Natural supplements for controlling diabetes
One of the most effective ways of keeping blood glucose levels in check is through regular exercise. Exercise aids the body in using glucose more efficiently, and it can even reduce blood glucose levels. Experts recommend that adults engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise weekly.
Another natural method of controlling blood glucose levels is through a healthy diet. Eating foods that are high in fibre, such as fruits, whole grains, and vegetables, can help regulate blood glucose levels. These foods slow down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels. Additionally, consuming foods that are high in protein, such as lean meats, fish, and nuts, can also help regulate blood glucose levels. [ How to control diabetes naturally?]
Staying well hydrated by drinking plenty of water is also vital for controlling blood glucose levels naturally. Dehydration can cause blood glucose levels to rise, so it is essential to stay hydrated. Drinking water can also help flush excess glucose out of the bloodstream.
Stress can also have an impact on blood glucose levels, and therefore, it is crucial to find ways to manage stress. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga can all help reduce stress and promote relaxation, leading to more stable blood glucose levels.
Getting adequate sleep is also crucial in regulating blood glucose levels. Lack of sleep can disrupt the body’s hormonal balance, leading to insulin resistance and elevated blood glucose levels. Experts recommend that adults should aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to maintain healthy blood glucose levels.
In addition to these lifestyle changes, certain natural supplements such as cinnamon, chromium, and magnesium may also help regulate blood glucose levels. However, it is important to consult a healthcare provider before taking any supplements as they may interact with other medications or have potential side effects.
Natural supplements for controlling diabetes
There are several natural supplements that may help control diabetes, although it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements as they can interact with other medications or have potential side effects. Here are some examples of natural supplements that may help:
1. Cinnamon: Some studies have suggested that cinnamon may help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. It can be added to foods or taken as a supplement.
2. Chromium: Chromium is a mineral that may help improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. It can be found in foods such as broccoli and grape juice, or taken as a supplement.
3. Magnesium: Magnesium is a mineral that may help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. It can be found in foods such as spinach, almonds, and black beans, or taken as a supplement.
4. Alpha-lipoic acid: Alpha-lipoic acid is an antioxidant that may help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. It can be found in foods such as spinach and broccoli, or taken as a supplement.
5. Gymnema Sylvestre: Gymnema Sylvestre is a herb that has been traditionally used in Ayurvedic medicine to treat diabetes. It may help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
6. Bitter Melon: Bitter melon is a fruit that has been used in traditional medicine to treat diabetes. It may help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
👉[Best method to control blood glucose naturally scientifically proven method]
It is important to note that while these natural supplements may help control diabetes, they should not be used as a substitute for medication or other recommended treatments. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop an individualised treatment plan for managing diabetes.
In conclusion, maintaining healthy blood glucose levels is essential to overall health. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, staying hydrated, managing stress, getting enough sleep, and certain natural supplements can all help regulate blood glucose levels naturally. By making these lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetes and other health problems associated with high blood glucose levels.
FAQs
1. What are diabetes blood sugar levels?
Blood sugar levels in diabetes refer to the amount of glucose in the blood of an individual with diabetes. The normal range for blood glucose levels is typically between 70 and 130 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) before meals, and less than 180 mg/dL 2 hours after starting a meal.
However, for individuals with diabetes, the target range for blood glucose levels may vary depending on the type of diabetes, age, overall health status, and other factors. Generally, for people with type 1 diabetes, the target range for blood glucose levels is 80-180 mg/dL, while for people with type 2 diabetes, the target range is 70-130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL 2 hours after starting a meal.
It is important for people with diabetes to regularly monitor their blood glucose levels to ensure they are within the target range. High blood glucose levels, also known as hyperglycemia, can cause a range of symptoms such as increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Over time, high blood glucose levels can also cause damage to organs such as the kidneys, nerves, and eyes.
On the other hand, low blood glucose levels, also known as hypoglycemia, can also be dangerous and cause symptoms such as shakiness, confusion, sweating, and dizziness. In severe cases, hypoglycemia can lead to seizures or loss of consciousness.
Managing blood glucose levels is a critical aspect of diabetes management, and individuals with diabetes should work with their healthcare team to develop a personalised plan for monitoring and controlling their blood glucose levels.
👉[Best method to control blood glucose naturally scientifically proven method]
2. What causes high blood sugar in diabetics?
In people with diabetes, high blood sugar levels occur when there is not enough insulin in the body or the body cannot use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps the body use glucose (sugar) for energy. When insulin is not functioning properly or is absent, glucose builds up in the blood instead of being used by the body’s cells for energy, resulting in high blood sugar levels.
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, while type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin to meet the body’s needs. Other factors that can contribute to high blood sugar levels in people with diabetes include illness, stress, certain medications, and eating too many carbohydrates or sugary foods.
3. How often should a person with diabetes monitor their blood sugar?
The frequency of blood sugar monitoring for people with diabetes can vary depending on the type of diabetes, the severity of the condition, and the treatment plan prescribed by their healthcare provider. In general, people with type 1 diabetes, who require insulin therapy, may need to monitor their blood sugar levels several times a day, such as before meals and at bedtime.
For people with type 2 diabetes who are managing their condition with lifestyle changes and/or oral medications, the frequency of blood sugar monitoring may be less frequent, such as daily or a few times a week. However, if blood sugar levels are difficult to control or if insulin therapy is required, more frequent monitoring may be necessary.
It is important for individuals with diabetes to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the appropriate frequency of blood sugar monitoring based on their individual needs and treatment plan. Regular monitoring can help individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about their diet, physical activity, and medication regimen to better manage their blood sugar levels and prevent complications associated with high or low blood sugar.
Doctor-formulated blood sugar supplement formulated using Ivy League research, and backed by real-world results
Live life free from fear
Where can I get effective natural supplement?
GlucoBerry™‘s proprietary formula is the first in the world to combine three clinically-proven blood-sugar-supporting nutrients with premium Maqui Berry extract. [Get it here]